War and Military
Reading Between the Lines of Israel-Palestine Conflict

flickr/zoriah
Amid the talks between Lebanese authorities and United Nations on the refugees from Palestine, a century old Israel-Palestine issue has again strike headlines. As the time has passed, this issue has become even more complex with the stubbornness of Arab world to agree on the norms of Saudi Arab Peace Plan 2002 by Israel and the threat to Israelites of becoming a minority in their own country. But whose country was it originally or is this whole conflict based on some superficial assumption? All this can be known after carefully dissecting the history of a land which has an equally important significance for Jews, Christians and Islam.

Jews claim that according to Bible, Moses led the Israelites to Palestine, now Israel and David (Abraham descendent) conquered Jerusalem in about 1000 BC establishing an Israelite kingdom. While at the same time Arabs draws the claim that Abraham’s son Ishmael being the forefathers of Arabs grant them the same right of land.
Jews claim that during 13th century Mamelukes (originally slave soldiers of Arabs based in Egypt) had invaded the land establishing an empire of Arab speaking Muslims. This was the time when the emigration of Jews started.
 Eventually Ottomans in 1517 invaded the land and Palestine became a part of Ottoman Empire which further led to reduction in the population of Jews, though during this duration there were no forced eviction as witnessed during the time of World War when Ottoman Empire joined Austria-Hungary and Germany against Allies and the Turkish military government had ordered the deportation of all foreign nationals.
Eventually Ottomans in 1517 invaded the land and Palestine became a part of Ottoman Empire which further led to reduction in the population of Jews, though during this duration there were no forced eviction as witnessed during the time of World War when Ottoman Empire joined Austria-Hungary and Germany against Allies and the Turkish military government had ordered the deportation of all foreign nationals.
This newfound hatred of Turkish governor turned Jews against the Ottoman Empire under whom Jews were thinking of creating a Jewish homeland earlier with the increasing impact of Zionist Movements. NILI, a Jewish espionage group network was formed to help Britishers during the World War 1.
Due to this insider information of Jews, Britishers were able to gain control over Ottoman Empire. In the exchange of this information, Jews tried to persuade Britishers for a Jewish state.
Seed of Arab-Israel Difference
Due to help of NILI, Britishers promised to bring the idea of Jewish state on the table while at the same time Sir Henry Macmohan secretly corresponded with Husayn ibn `Ali, the patriarch of the Hashemite family and Ottoman governor of Mecca and Medina to win the war and promised him Hashemite rule in independent Arab state. The Arab revolt, led by T.E Lawrence, the famous story of Lawrence of Arabia and Husayn’s son Faisal was successful in defeating Ottomans. Another secret agreement, was a deal between Britain and France to carve up the Arab provinces of the Ottoman Empire and divide control of the region which eventually led to the formation of The British Mandate and The French Mandate.
After winning the war, Lord Arthur Balfour issued a declaration called Balfour declaration announcing government’s support of Jewish national home in Palestine. In 1921, the region was divided in two: east of the Jordan River which became Emirate of Transjordan to be ruled by Faysal’s brother Abdullah and west of Jordan became Palestine Mandate. Throughout the region, Arabs were angered by Britain’s failure to fulfil its promise to create an independent Arab state, initiating the modern history of claim of land. This anger fuelled by the misgovernance of British and French rule with the Wailing Wall Conflict triggered the first Arab revolt in Palestine (1936-1939) where primarily urban and elitist Higher Arab Committee (HAC) revolted followed by a violent peasant led revolution where rebellions were brutally suppressed by British army for controlling the situation.
Wailing Wall Conflict: In 1928, Muslims and Jews in Jerusalem began to clash over their respective communal religious rights at the Wailing Wall (al-Buraq in the Muslim tradition). The Wailing Wall, the sole remnant of the second Jewish Temple, is one of the holiest sites for the Jewish people. But this site is also holy to Muslims, since the Wailing Wall is adjacent to the Temple Mount (the Noble Sanctuary in the Muslim tradition). On the mount is the site of the al-Aqsa Mosque and the Dome of the Rock, believed to mark the spot from which the Prophet Muhammad ascended to heaven on a winged horse.
On August 15, 1929, members of the Betar youth movement (a pre-state organization of the Revisionist Zionists) demonstrated and raised a Zionist flag over the Wailing Wall. Fearing that the Noble Sanctuary was in danger, Arabs responded by attacking Jews throughout the country
With the Nazi propaganda gaining ground in 1939’s Germany of Adolf Hitler, the killing of Jews (holocaust) and horrors of concentration camps, there was an increased immigration of Jews to the Palestine Mandate, which was a trigger to Arab Conflict during the same period. This increase led to the issue of White policy paper which restricted the immigration of Jews to a 75000 in the next five years triggering pressure from Zionist group from all around the world.Even after this due to Holocaust, the illegal immigration continued eventually increasing the population of Jews in the Palestine mandate from 1% to 35% and it was during this time that Zionist leadership met in New York City for Biltmore declaration in support of a Jewish Commonwealth. With the outbreak of World War 2, British freed Jewish underground leaders in amnesty. Eventually angry with the White Paper policy some underground groups attacked Britishers.
Sensing the situation getting out of control and also by the end of WWII, the British military power had been exhausted completely; the matter was taken to United Nations where United Nations Partition plan was formulated on the basis of population residing of Arabs and Jews residing within the borders of Mandate of Palestine.
The Contention By Arabs
Jewish state was larger in the UN plan i.e.56 % to 43% allotted to Arabs assuming the Jewish immigration. Jerusalem and Bethlehem were declared the international cities. One major contention in this Partition plan was the commonality of land as there were certain areas in the Arab state which had Jewish control and vice versa. Initially the availability of less land to Arabs and this common place issue fueled the rage among Arab Palestinians and as soon as the British army withdrew from Jewish Mandate, it became a no man’s land and taking advantage of the situation, Jews proclaimed the independence of Israel and Arab invaded Israel to get rid of Jews from the region.
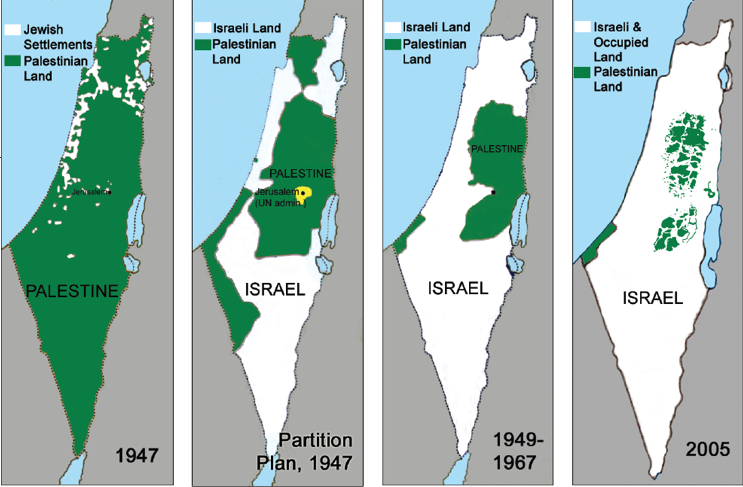
The outcome of the first Arab-Israeli war of 1948 was uncertain initially (though due to organized Zionist movements and militias like Betar youth movement ETZEL, Haganah and Palmach Israel had an upper hand over Arabs who had lost in the Arab revolt earlier and were crushed by British with no significant organization to tackle the war), but after arms shipments from Czechoslovakia reached Israel, its armed forces established superiority and conquered territories beyond the UN partition plan borders of the Jewish state, almost 65 percent of the total Palestinian land. This war further led to 6 day war in 1967 and Yom Kippur War of 1973, through which the land acquired by Israel remained almost the same, sometimes even increasing as it happened later during invasion in Lebanon, every time Arab countries facing a defeat and seizure of lands.
This history of the land is the line of contention responsible for numerous accords like Camp David Accord, Oslo Accord, various armistice ceasefires between Israel and Arab countries and in the modern day conflict rise of extremists groups like Hamas and weakening of authorities of PNA (Palestinian National Authorities), increasing number of Palestinian refugees in countries like Syria, Jordan and Lebanon.
War and Military
How are Light Armored Vehicles Protected on the Battlefield?

When most people picture a military armored vehicle, they immediately think of the Main Battle Tank, a key player in battlefields around the world. But the Main Battle Tank is not the primary mobile platform for servicemen and women. Instead, that is the Light Armored Vehicle: a military vehicle that’s speedier and more agile than a tank, while offering far greater levels of armored protection, firepower, and maneuverability than a civilian vehicle such as a 4×4.
In order to be fit for purpose, Light Armored Vehicles must measure up to rigorous measures, including STANAG 4569, an assessment that shows their ability to deal with kinetic energy, artillery, and IED attacks. But how exactly do modern Light Armored Vehicles protect themselves on the battlefield? Here are five of the key attributes shared by today’s most popular vehicles.
It’s all about the armor
A Light Armored Vehicle’s name suggests that, well, it’s lightly armored. In fact, that’s something of a misnomer. A Light Armored Vehicle may not be quite the heavy-duty bruiser that a Main Battle Tank is, but don’t make the mistake of thinking that a vehicle such as this doesn’t boast some impressive protection in case it’s hit during an attack. While its armor plating is not as formidable as a Main Battle Tank, the standard model LAV-25 (the Light Armored Vehicle most widely used by the U.S. Army and Marines, alongside other armies around the world) still boasts light gauge high hardness welded steel armor that offers effective protection against small arms rounds, without adding unnecessary weight.
Its impressive suspension system also promises improved survivability against IEDs. Some of the current models of LAVs have been in service since the 1980s. But there have been upgrades, such as the LAV-25 A2, which offers increased external and internal ballistic armor upgrades, including protection from fearsome 14.5 mm armor-piercing rounds. When the LAV-25 models are superseded sometime this decade, armor-driven survivability will be one of the big areas that will get an overhaul. New breakthroughs in materials science are opening up fresh avenues for exploration in armor that is lighter weight, but tougher than existing forms of armor plating currently in use.
Blast-resistant seating
The increased use of improvised explosive devices (IEDs) as part of asymmetric warfare is a trend that has transformed battlefields over the past two decades. To protect the lives of crew travelling in Light Armored Vehicles, along with other combat vehicles, special blast-attenuating seats have been installed. Some manufacturers produce potentially lifesaving seating options to fit all crew positions, including commander, gunner, driver and troop seats.
Smart sensors
Protection can mean armoring. It can also mean ways to avoid risking taking hits in the first place. Fortunately, smart sensors have come on a long way in recent years — and make this second option more viable than ever. Modern Light Armored Vehicles increasingly boast sensors designed to sense, classify, track, and defeat incoming threats. One example is their impressively sensitive radar and jamming technologies. These can be used to counter threats like drones by severing the link between the drone and its controller, causing them to crash out of the sky. This may be vital in scenarios where an attack may involve weaponry a Light Armored Vehicle would not be able to adequately defend against with its existing armor. Sensing the threat ahead of time means being able to take proactive steps to counter and avoid it.
The best defense is a good offense
Smart sensors are one proactive way for Light Armored Vehicles to protect themselves. Another is using offensive weapons. The LAV-25 boasts a two-person powered turret fitted with a 25 mm M242 “Bushmaster” chain gun. Internally, it features firing ports which can allow six fully-equipped infantrymen to defend the vehicle using personal weapons. There is additionally a 7.62mm machine gun in co-axial mounting for carrying out anti-infantry defense. If required, a second 7.62mm machine gun can also be mounted along the turret roof. Variations of the LAV-25 can be — and have been — fitted with anti-tank guided missiles, superior unmanned turret, mortars, 5-barreled Gatling cannons, Stinger missiles, smoke grenade dischargers, and more. Though Light Armored Vehicles are not intended to replace a Main Battle Tank, these vehicles can more than hold their own in the field of combat when required. And, as many a good strategist has noted, the best defense is a good offense.
Tires
Compared to the tracks used by Main Battle Tanks, Light Armored Vehicles far more closely resemble civilian 4x4s. But the rigors of travelling in warzones is very different to the requirements of driving on even the toughest of terrains in the civilian world. One of the key points of protection for a Light Armored Vehicle is its ability to easily traverse difficult terrain. That comes in handy when you’re avoiding threats such as IEDs which make travelling along ordinary roads prohibitive. Features such as Central Tire Inflation Systems (CTIS) help these military vehicles with better all-wheel drive performance and mobility. Many have a “limp home” feature that can allow them to carry out limited travel even in the event of major tire leaks. That avoids the risk inherent with a Light Armored Vehicle being rendered totally disabled on the battlefield.
Technology
Concerns and Limitation of Cyber Warfare

The discovery of Stuxnet, a malware that targeted a nuclear facility, was somewhat revolutionary and groundbreaking. It targeted ICS which monitor and run industrial facilities. Before that, most of malicious programs were developed to steal information or break-in into financial sector to extort money. Stuxnet went beyond went and targeted high-level facilities. It is not hard to imagine what damage it could have inflicted if the worm were not detected. What is more worrisome, the technology is out. It might not be perfect, but it is definitely a start. Regardless of the intentions behind Stuxnet, a cyber bomb has exploded and everyone knows that cyber capabilities indeed can be developed and mastered.
Therefore, if they can be developed, they will probably be. The final goal of Stuxnet was to affect the physical equipment which was run by specific ICS. It was done in order to manipulate computer programs and make it act as an attacker intended it to act. Such a cyberattack had a particular motivation; sabotage of industrial equipment and destruction could have been one of the goals. So, if they were indeed the goals, it might have been an offensive act, conducted by an interested party, presumably, a state for its political objective. Yet, there are certain limitations when it comes to so-called “cyber weapons” (malware that might be employed for military use or intelligence gathering).
One of the main concerns of cyber offence is that code may spread uncontrollably to other systems. In terms of another physical weapon, it is like a ballistic missile that anytime can go off-course and inflict damage on unintended targets and/or kill civilians. Cyber offensive technology lacks precision, which is so valued in military. For example, in ICS and SCADA systems one may never know what can backfire because of the complexity of the system. The lack of precision consequently affects military decisions. When launching a weapon, officers should know its precise capabilities; otherwise, it is too risky and is not worth it.
In case of Stuxnet, the program started replicating itself and infected computers of many countries. For this moment we do not know if it were planned in that way. However, provided that that target was Natanz facility, it is unlikely. Symantec Corporation started analyzing the case only with external help; it did not come from Natanz. This exacerbates the case if a country decides to launch an offensive cyberattack.
If the military planning cannot prevent cyber technology to go awry or to go out in the public, it brings more disadvantages than advantages. Moreover, given a possibility of the code being discovered and broke down to pieces to understand what it does, it may potentially benefit an opposing party (and any other interested party along the way). This is unacceptable in military affairs.
Similarly, when the code is launched and it reaches the target, it can be discovered by an opponent. In comparison to nuclear, when a bomb explodes, it brings damage and destruction, but its technology remains in secret. In case of cyber, it may not be the case, as when a malware/virus is discovered, it can be reverse engineered to patch vulnerability. By studying the code, an enemy would find out the technology/tactics used that could be unfavourable in the long-run for the attacker.
Additionally, it should be said that not every malware is meant to spread by itself. In order to control the spread, vulnerability can be patched, meaning updating the software which had that vulnerability. An anti-malware can also be introduced; this will make the computer system immune to that particular vulnerability. Nonetheless, if the malware spreads uncontrollably, there is nothing much that an attacker can do. It is not possible to seize the attack. In this scenario, an attack may only release information about this certain vulnerability so that someone else can fix it. However, a state is highly unlikely to do so, especially if the damage is extensive. It would not only cost the state diplomatic consequences, but also it might severely impact its reputation.
An AI-enabled cyberattack could perhaps fulfill its potential. That means involvement of artificial intelligence. AI systems could make digital programs more precise, controlling the spread. In contrast, it could also lead to a greater collateral damage, if a system decides to target other facilities that may result in human death. Similar concerns are raised in the area of autonomous weapon systems in regard to the need of leaving decision-making to humans and not to technology. AI technology has a potential to make existing cyberattacks more effective and more efficient (Schaerf, 2018).
Aforementioned concern leads to another and affects the end result. When a certain weapon is employed, it is believed to achieve a certain goal, e.g. to destroy a building. With cyber capabilities, there is no such certainty. In the
Alternatively, the true costs of cyberattacks may be uncertain and hard to calculate. If that is so, an attacker faces high level of uncertainty, which may also prevent them from a malicious act (particularly, if nation states are involved). However, the costs and the benefits may always be miscalculated, and an attacker hoping for a better gain may lose much more in the end (e.g. consider Pearl Harbour).
Another concern refers to the code becoming available to the public. If it happens, it can be copied, re-used and/or improved. Similar concerns in regards to proliferation and further collateral damage emerged when Stuxnet code became available online. An attacker may launch a cyberattack, and if it is discovered, another hacker can reverse engineer the code and use it against another object. Moreover, the code can be copied, improved and specialized to meet the needs of another party. Technology is becoming more complex, and by discovering a malware developed by others, it also takes less time to produce a similar program and/or develop something stronger. (For instance, after Stuxnet, more advanced malwares were discovered – Duqu and Flame).
Furthermore, there are other difficulties with the employment of cyber offensive technology. In order to maximize its result, it should be supported by intelligence. In case of Stuxnet, an offender needed to pinpoint the location of the facility and the potential equipment involved. It has to find zero-days vulnerabilities that are extremely rare and hard to find[1]. Cyber vulnerability is all about data integrity. It should be reliable and accurate. Its security is essential in order to run an industrial infrastructure.
After pinpointing vulnerability, security specialists need to write a specific code, which is capable of bridging through an air-gapped system. In case of Stuxnet, all of abovementioned operations required a certain level of intelligence support and financial capability. These complex tasks involved into development were exactly the reason why Stuxnet was thought to be sponsored and/or initiated by a nation state. If intelligence is lacking, it may not bring a desirable effect. Moreover, if cyber offense is thought to be used in retaliation, malicious programs should be ready to use (as on “high-alert”) in the event of necessity.
Regardless of some
advantages of cyber offence (like low costs, anonymity etc), this technology
appears to be unlikely for a separate use by military. There is a high level of
uncertainty and this stops the army of using technology in offence. Truth is
when you have other highly precise weapons, it does not make sense to settle
for some unreliable technology that may or may not bring you a wanted result.
Yet, other types of
cyberattacks like DDoS attacks can give some clear advantages during military
operations and give an attacker some good cards in case of a conflict. When
such attacks used together with military ground operations, they are much more
likely to bring a desired result.
[1] For better understanding, out of twelve million pieces of malware that computer security companies find each year, less than a dozen uses a zero-day exploit.
War and Military
Swedish subs: a relic of the past?
As part of the program to replace its four Walrus-class submarines, the Dutch government is examining offers submitted by four European companies. It will announce by the end of the year which two competitors have been selected for the next negotiation stage.
Last June, Swedish Saab Kockums and Dutch partner Damen unveiled an initial design of submarine as part of their proposal to replace the Dutch Royal Navy’s fleet. During the European naval show in October, they further revealed technical details about their offer. Despite these announcements, Saab Kockums appears far from being able to draft more than drawings as it lacks the technology and manpower required to build submarines.
Kockums, a Swedish shipyard now known as Saab Kockums, made international headlines back in the 1990s when it closed a major deal with the Australian Navy to design their submarines fleet. Since then, the company seems to have become an empty shell.
In 2005, to strengthen its market position, Kockums joined its German competitor TKMS. Their partnership soon deteriorated as Kockums failed to attract new clients and retain old ones. The A26-class Kockums was developing did not sell well on the international market. Designed in the early 1990s, this sub class was considered outdated and too pricy. In 2013, after 20 years of cooperation, Kockums lost a contract with Singapore. Although TKMS eventually managed to win that contract thanks to another subsidiary, it led to increased tensions between the two companies.
In 2014, Russia’s realpolitik and the Ukrainian crisis led the Swedish government to reconsider its naval capabilities. The government realized the capacity to build submarines was of strategic importance, calling for Swedish companies to maintain an adequate level of competency. The Parliament decided to renew its subs fleet and promote local skills by ordering two updated ersatz of the A26-class to Kockums. However, the Swedish government failed to agree on the price with TKMS, ending the negotiation. At the height of the crisis, Swedish military authorities stormed Kockums’ laboratory in Sweden to retrieve technology that, according to them, belonged to the army. After that incident, deemed unusual by military experts, TKMS entered talks with Saab to sell Kockums. The sale was eventually closed later that year.
Over the past decades, U-boots have evolved from a fighting device to a diplomatic, sovereignty and intelligence tool. It is now used to locate enemies, deploy elite troops, collect data and send political messages. They require cutting-edge technology and constant research and development. Of all naval solutions, designing subs poses the greatest technical challenges and hence require special skillsets. Not keeping up with the fast-changing evolutions can quickly become the death knell of subs’ designers. Though Kockums prove to be a competitive submarine maker in the 1990s, not constructing subs over the last two decades means they have lost their technical and technological expertise. The price at which the company was sold is quite revealing. First thought to be worth 1 billion kronor, Kockums was sold for 340 million kronor (US$ 50,4 million).
The Dutch Navy is internationally recognized for the role its subs played in reducing piracy in the Gulf of Aden. It is part of the few countries able to furtively navigate oceans. The construction of its new submarine fleet is scheduled to start in 2021 and be operational by 2027. Saab Kockums is offering its updated A26-class and it might not be able to meet the deadlines. The A26-class has never been built before and, even if its design has been updated, the scope of the technical adjustments needed for this class to function smoothly is not yet known. With the technology used in naval solutions rapidly evolving, it might as well be less time-consuming to develop an entirely new class rather than update an ancient model.
Moreover, there are doubts about Saab Kockums’ capacity to continue its activities in a few years from now. The company already inked several deals with the Swedish Navy. However, to be able to keep up with the investments needed in research and development, Saab Kockums must succeed on export markets. If it fails to secure multiple deals abroad, it will eventually go bankrupt. With such scenario, betting on them might not be the smartest move.
The future does not look bright for Saab Kockums. Though signing with the Dutch Navy could temporarily be good news for them, without sustainable investments in research it will go down like a lead zeppelin!
-

 Business11 months ago
Business11 months agoHow To Future-Proof Your Business With The Right Tools
-

 Travel9 months ago
Travel9 months agoTravelling from San Antonio to Guadalajara
-

 Business12 months ago
Business12 months agoWhat are EDC products, and why should you always have them?
-

 Travel6 months ago
Travel6 months agoTravel wellness tips for a healthier and more enjoyable journey
-

 Europe4 months ago
Europe4 months agoRecent Books by Boaventura de Sousa Santos: Law, Colonialism, and the Future of Europe